Section: New Results
Action Detection in Untrimmed Videos
Participants : Abhishek Goel, Michal Koperski, François Brémond.
Problem Statement
The problem addressed in this work is Online Action Detection in Untrimmed Videos. The task of action detection can be broken down into two major modules, namely Action Recognition module and Temporal Localization module. Action Recognition module is responsible for assigning an action label to a trimmed video clip that is having only one action from start to the end of the clip. Temporal localization module on the other hand is responsible for deciding upon the start and end of the action present in an untrimmed video. The work has been done on the Smarthomes Dataset [22].
Action Detection Framework
-
Recognition Module: The recognition module used in this work, makes use of trajectory features [72], [128] for describing the input frames. These features are clustered using a 512 centroid Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and encoded using Fisher Vector. Finally Fisher Vectors are then used as input to SVM classifier, which is trained in a one vs all fashion. Figure 19 gives an overview of the recognition model used in this work.
Figure 19. Steps involved in the action recognition part of the Action Detection Module. The first step is to detect the feature points in the input image. Since, in the feature detector used is Dense Trajectories [128], the feature points have been obtained using dense sampling followed by removal of points in homogeneous points. For each of the interest point, HOF descriptor is computed. These features are then clustered using GMM and encoded using fisher vectors. Finally, a SVM classifier is trained using the fisher vectors obtained for different video clips of different action class. 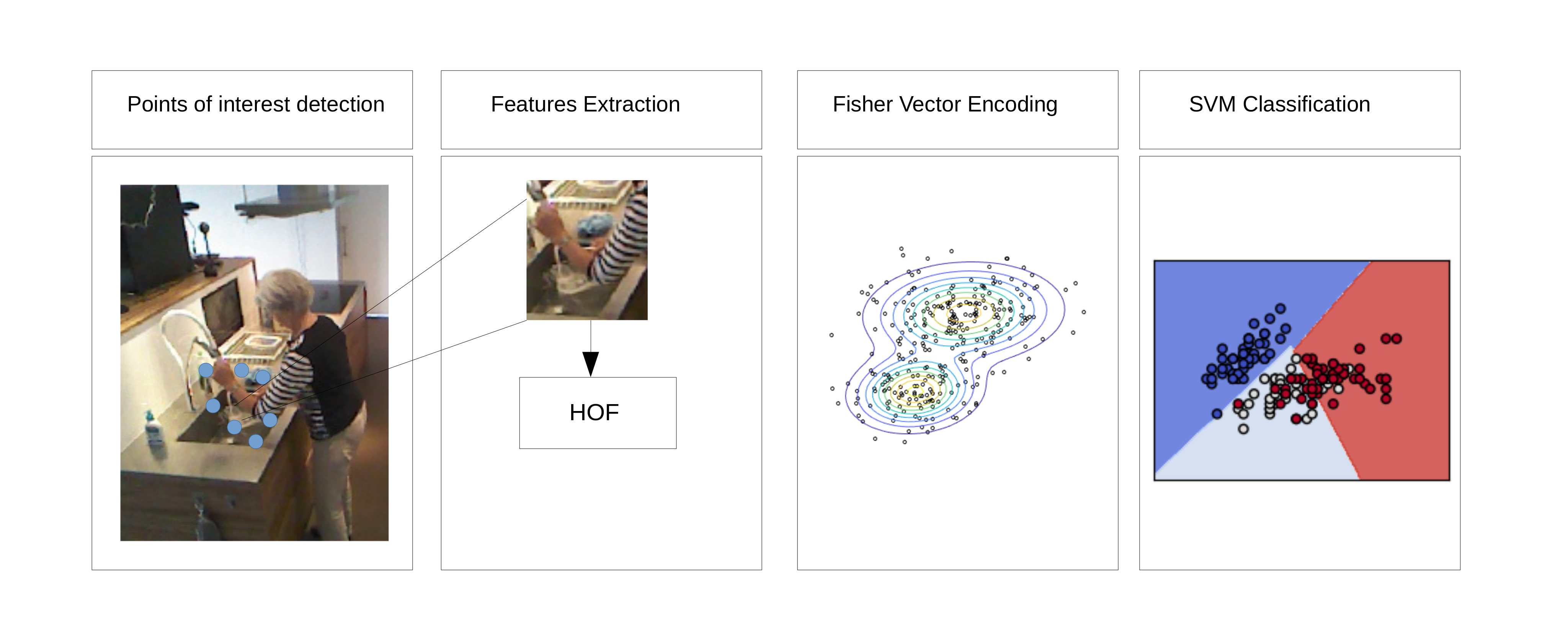
-
Temporal Localization Module: The temporal localization module makes use of a sliding window architecture [72], [101], [120], [97], [134] to give candidate clips, intervals which might have action of interest, to the action recognition module to get the label for that interval.
Challenges
The major challenges when working with untrimmed videos in an online fashion are to identify the intervals where there are No Action of interest present and to identify the transition from the No Action interval to an interval containing an action of interest. In order to address these two problems, two new methods were proposed.
Proposed Methods
Distance Based Sliding Window
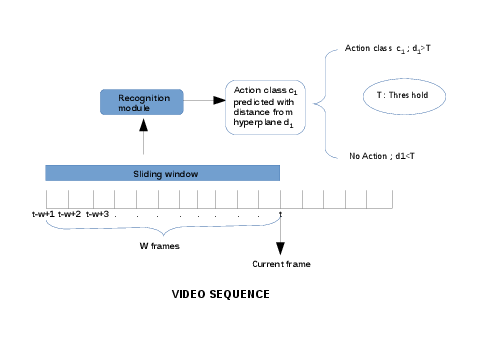
The first method, named "Distance Based Sliding Window" defined an actioness criterion based on the distance of a Fisher Vector from the hyperplane of a class of a trained classifier to address the problem of identifying the No Action intervals. Figure 20 gives an overview of the proposed approach.
|
Past and Future Windows
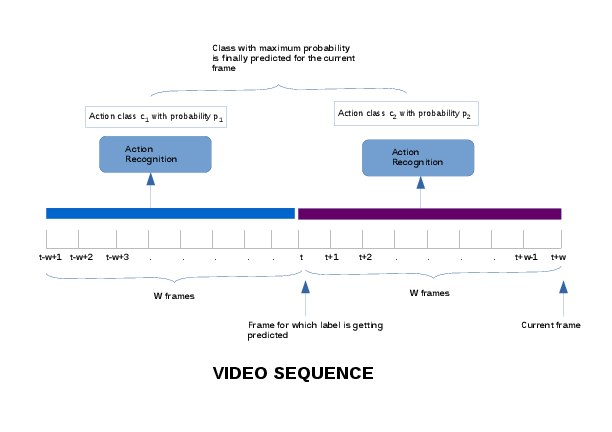
The second method, named "Past and Future Windows" addressed the second issue with a sliding window architecture which makes use of some of the future frames in order to get an action label for the current frame. The task is to perform Online Action detection in which ideally we have information only about the frames that have been seen till now and prediction for the current frame has to be done on the basis of this information. The term "future" refers to the frames which come after the frame in consideration. Since now the label is getting predicted for a frame after seeing some more frames after it, a delay is introduced in the prediction of the label. This delay is equivalent to W frames, where W is the window size. Figure 21 gives an overview of the proposed method.
|